Explain How Atmospheric Pressure Differences Create Winds
Hemisphere with CCW flow around lows CW around highs High to Low pressure deflection to left in S. Pressure always decreases vertically with height Air pressure is exerted equally in all directions.
This is called pressure gradient force.

. At the Equator the sun warms the water and land more than it does the rest of the globe. Air that moves horizontally between high and low pressure zones makes wind. Because of Earths spin and the Coriolis effect winds of a low pressure system swirl counterclockwise north of the equator and clockwise south of the equator.
List the three major categories of atmospheric circulation and give at least one example of each. What is the difference between the windward and the leeward sides of a mountain range. As air rises the pressure lowers and surrounding air moves in to replace it causing wind.
Air expands when heated and gets compressed when cooled. Side facing the wind it rises and begins to experience adiabatic cooling. This is a low-pressure system.
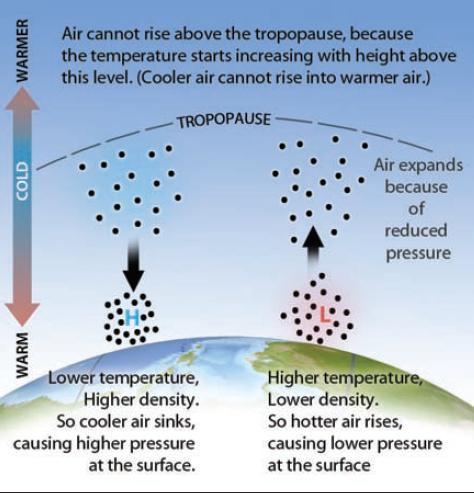
Changes in air pressure are caused by differences in air temperature above the earth and the temperature of an air mass is determined by its location. The movement of air from warm to cold. Atmospheric Pressure In the presence of the pressure gradient force the air will be forced to move wind Winds flow from an area of higher pressure to an area of lower pressure Isobars lines of constant pressure Winds usually flow across isobars.
When a difference in atmospheric pressure exists air moves from the higher to the lower pressure area resulting in winds of various speeds. Air in horizontal motion is wind. This results in variations in the atmospheric pressure.
Air temperature differences create wind and cause pressure systems to develop. Warm equatorial air rises higher into the atmosphere and migrates toward the poles. On weather maps a low pressure system is labeled with red L.
That pressure is called atmospheric pressure or air pressureIt is the force exerted on a surface by the air above it as gravity pulls it to Earth. Warm air rises creating a low pressure zone. The more the pressure changes over a given distance usually the faster the wind will be.
At the same time cooler denser air moves over Earths surface toward the Equator to. The wind moves pressure systems and. Cause of Most Wind.
Under these conditions lows normally produce clouds precipitation and other turbulent weather such as tropical storms and. Atmospheric pressure also determines when the air will rise or sink. Chapter 4 Atmospheric Pressure and Wind Understanding Weather and Climate Aguado and Burt ATMO 1300 Pressure Pressure amount of force exerted per unit of surface area.
A high pressure system has higher pressure at its center than the areas around it. Hemisphere with CW flow around lows CCW around highs Upper-level pressure distribution is determined by temperature. The force that creates these changes in air pressure is known as the Pressure Gradient Force and is driven by changes in the temperature of the earths surface.
The difference in pressure over a distance is called a pressure gradient and this creates a force called the pressure gradient force simply that air wants to move from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure which is the driving force behind wind. Convection in the atmosphere creates the planets weather. Wind Wind results from a horizontal difference in air pressure and since the sun heats different parts of the Earth differently causing pressure differences the Sun is the driving force for most winds.
Pressure Gradient Force PGF - causes horizontal pressure differences and winds 2. As the Sun unevenly heats the surface of the Earth air rises and sinks resulting in high and low regions of air pressure. Differences in atmospheric pressure generate winds.
Both wind shear turbulence and convective turbulence cause drag which results in the ABL wind being slower than geostrophic subgeostrophic and causes the wind to cross isobars toward the low pressure. The wind is a result of forces acting on the atmosphere. Allows a variety of genes to exist amongst one another and in their environment and create different.
Cool air sinks creating a high pressure zone. A low-pressure system also called a depression is an area where the atmospheric pressure is lower than that of the area surrounding it. Pressure differences because of temperature differences due to the unequal heating of the earths surface.
Wind is determined by pressure Fast wind where isobars are close lg. The differences in atmospheric pressure causes the movement of air from high pressure to low pressure setting the air in motion. This is called cyclonic flow.
The air around you has weight and it presses against everything it touches. The wind is caused by differences in atmospheric pressure which is mainly caused by temperature difference. PGF High to Low pressure deflection to right in N.
For example air masses above oceans are typically cooler than air masses above continents. Gravity creates air pressure through the compression of the atmosphere. Pressure is the force exerted on a unit area and atmospheric pressure is equivalent to the weight of air above a given area on Earths surface.
Explain why atmospheric pressure decreases as altitude increases. This is best illustrated in a diagram of a sea breeze. Balanced wind in the atmospheric boundary layer ABL occurs when there is a balance between the pressure gradient force Coriolis force and the frictional drag force.
Lows are usually associated with high winds warm air and atmospheric lifting. The driving force behind changes in air pressure and therefore the creation of wind is gravity. The greater the pressure difference between the pressure zones the faster the wind moves.
Wind exists because of horizontal and vertical differences gradients in pressure yielding a correspondence that often makes it possible to use the pressure distribution as an alternative representation of atmospheric motions. Winds blow away from high pressure. Atmospheric pressure is commonly measured with a barometerIn a barometer a column of mercury in a glass tube rises or falls as the weight of.

What Is Wind Wind Is Air In Motion Differences In Air Pressure More Of A Difference In Pressure Faster Winds Lots Of Difference Ppt Download

(219).jpg)
No comments for "Explain How Atmospheric Pressure Differences Create Winds"
Post a Comment